Body
Get to know your body through a better understanding of your anatomy and find the answers to some of your most common questions.
Back
All topics

4 resources
19 resources

6 resources

4 resources

6 resources
Back
All topics

9 resources

12 resources

4 resources

11 resources

2 resources
Back
Back
All topics
17 resources
11 resources
17 resources

2 resources

Mauj Products
We’ve designed our products to help you explore your body, solo or otherwise. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned explorer, this is for you.
Back
All topics

4 resources

19 resources

6 resources

4 resources

6 resources
Back
All topics

9 resources

12 resources

4 resources

11 resources

2 resources
Back
Back
All topics

17 resources

11 resources

17 resources

2 resources

Mauj Products
We’ve designed our products to help you explore your body, solo or otherwise. Whether you’re a curious novice or a seasoned explorer, this is for you.
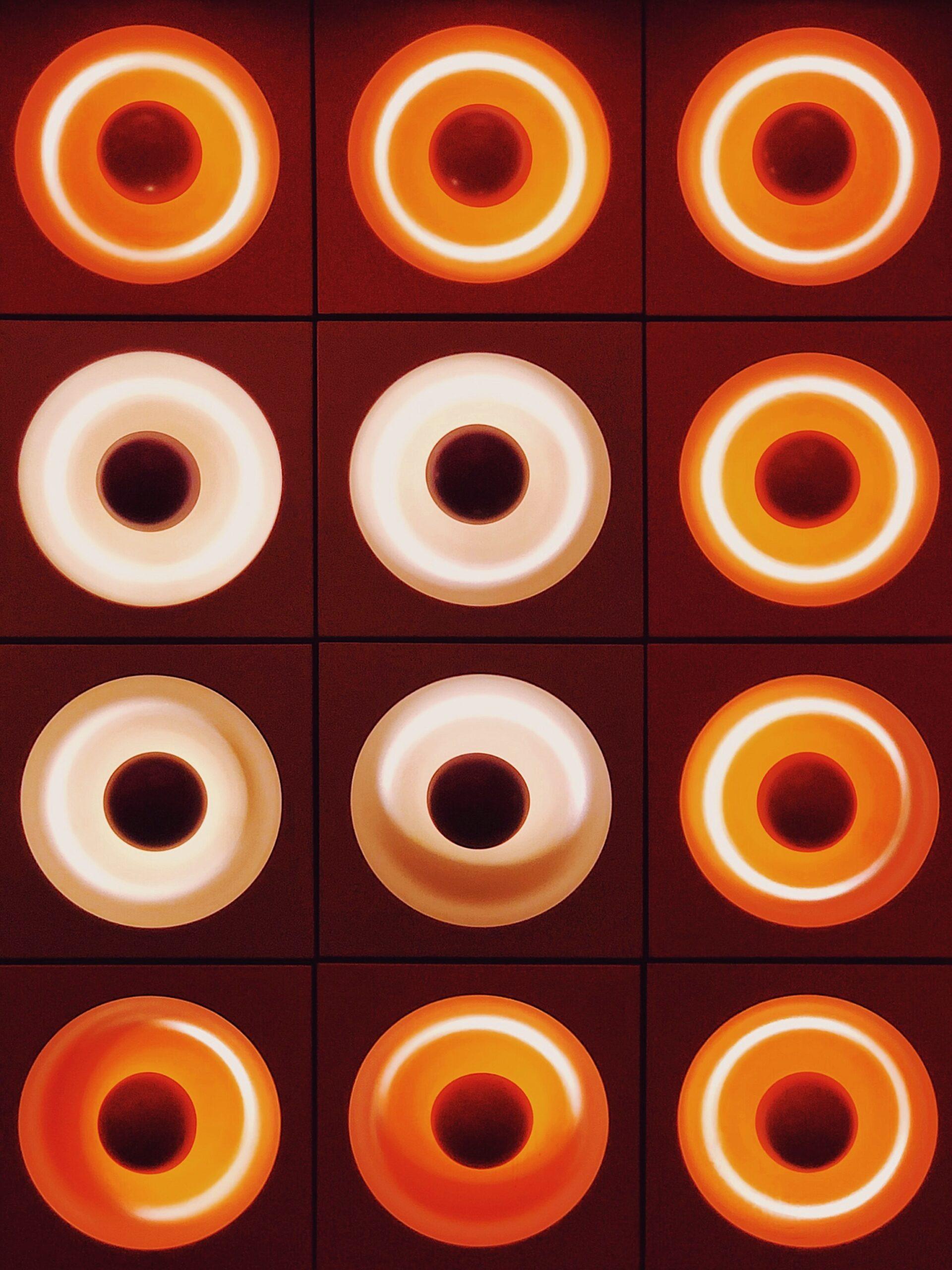
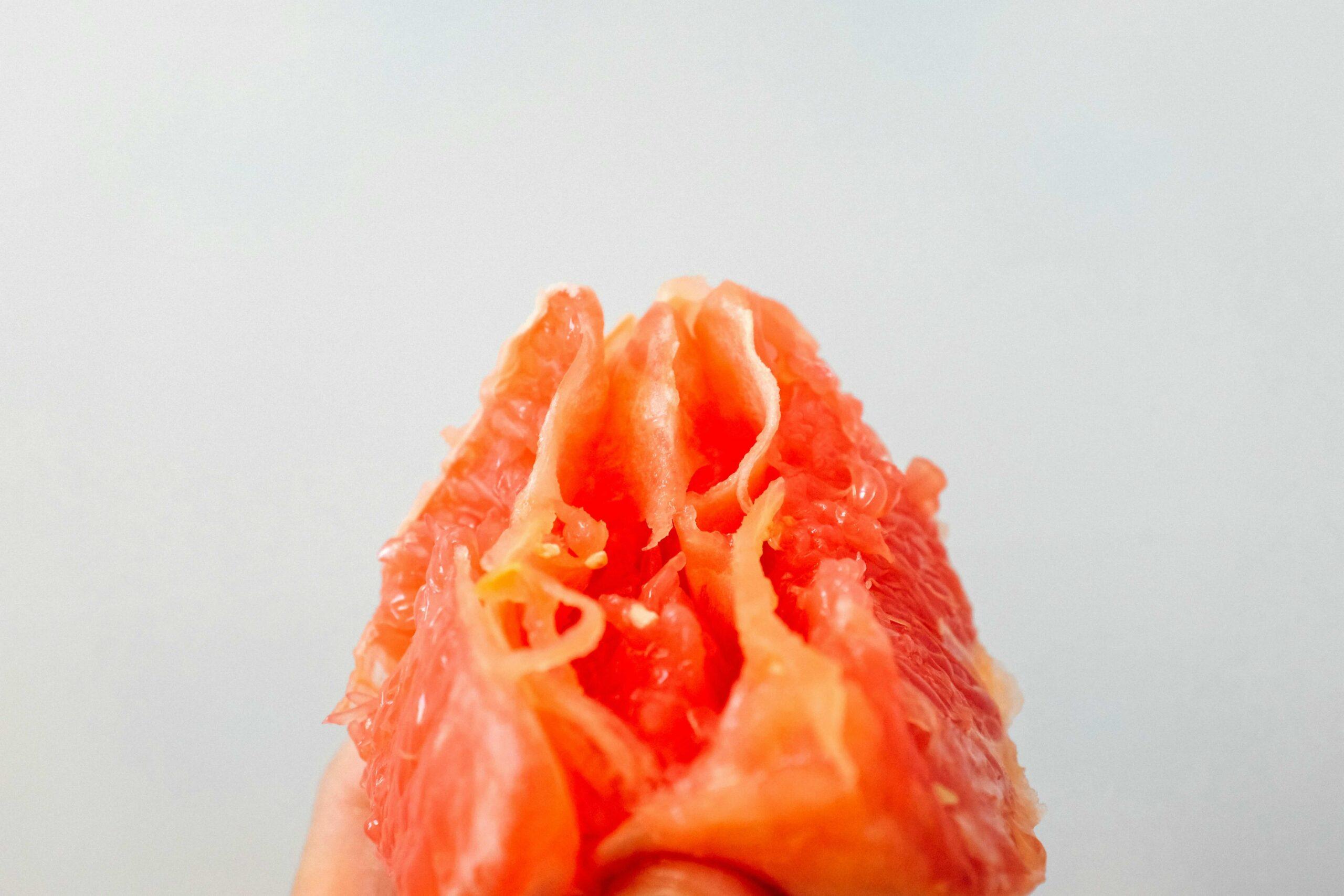
The cervix is a small yet very mighty organ that does so much for the female body. Let's learn more about this magical pathway.

Your cervix sits at the lowest point of the uterus (your womb) and acts as a passage between the vagina and the rest of the uterus. It is about 3 to 4 cm in length. When seen from below, it looks like a pink donut. Cervix is derived from the Latin word ‘collard’, which means neck.
The hole of the cervix is called the external os. So many things come in and out of this little hole, including menstrual blood, sperm, IUDs, and babies.
Where do we even start...
Due to the hormonal changes throughout the menstrual cycle, the positioning of the cervix, along with the fluids it produces, changes.
Estrogen is the hormone responsible for pulling the cervix up. As estrogen levels peak right before ovulation, the cervix is pulled up. Estrogen also makes mucus thin and more basic, making it friendly to semen around ovulation. Estrogen drops at ovulation, along with the cervix, right after the egg is released.
Progesterone then starts to rise, making the cervical mucus thick and more acidic, acting as a barrier to keep sperm out.
These changes can also impact sensations during sex, and you may find that certain positions are more or less comfortable and pleasurable for you at different times of your cycle. Similarly, while some women may experience heightened pleasure or even cervical orgasms from the stimulation of the cervix, for others the sensation is uncomfortable.
Even if you can’t see it, there are a few crucial measures you can take to keep your cervix healthy, which in part will help you stay healthy.
Did you find the answer you were looking for? Is there something we missed? What did you think of this resource? We want to hear from you.